Decoding Moz Page Speed: A Comprehensive Guide to Website Optimization
In today’s digital landscape, website speed is not just a luxury; it’s a necessity. A slow-loading website can lead to frustrated users, high bounce rates, and ultimately, lost revenue. Search engines like Google also factor page speed into their ranking algorithms, making it a critical component of any successful SEO strategy. This is where understanding and optimizing your Moz page speed becomes crucial. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding, measuring, and improving your website’s page speed using Moz’s tools and insights.
Why Moz Page Speed Matters
Before diving into the specifics of Moz’s tools, let’s understand why page speed is so important. A faster website offers numerous benefits:
- Improved User Experience: Users expect websites to load quickly. A delay of even a few seconds can significantly impact their experience.
- Lower Bounce Rate: Visitors are more likely to leave a slow-loading website, increasing your bounce rate.
- Higher Conversion Rates: Faster websites lead to better conversion rates, as users are more likely to complete purchases or sign up for services.
- Better Search Engine Rankings: Google considers page speed a ranking factor. Optimizing your Moz page speed can improve your search engine visibility.
- Mobile-First Indexing: With the increasing use of mobile devices, Google prioritizes mobile-friendly websites. Page speed is a key aspect of mobile optimization.
Understanding Moz’s Page Speed Tools and Metrics
Moz offers a variety of tools and resources to help you analyze and improve your website’s page speed. While Moz doesn’t have a dedicated “page speed tool” like Google’s PageSpeed Insights, its suite of SEO tools provides valuable insights into factors affecting page speed. These tools include:
- Moz Pro: Moz Pro is a comprehensive SEO platform that offers site crawls, rank tracking, keyword research, and link analysis. While it doesn’t directly measure page speed, it identifies technical SEO issues that can impact it.
- MozBar: The MozBar is a free browser extension that provides instant SEO metrics for any webpage, including domain authority, page authority, and spam score. Although it doesn’t directly show page speed, it provides insights into the overall health and authority of your website, which can indirectly affect your ranking and traffic.
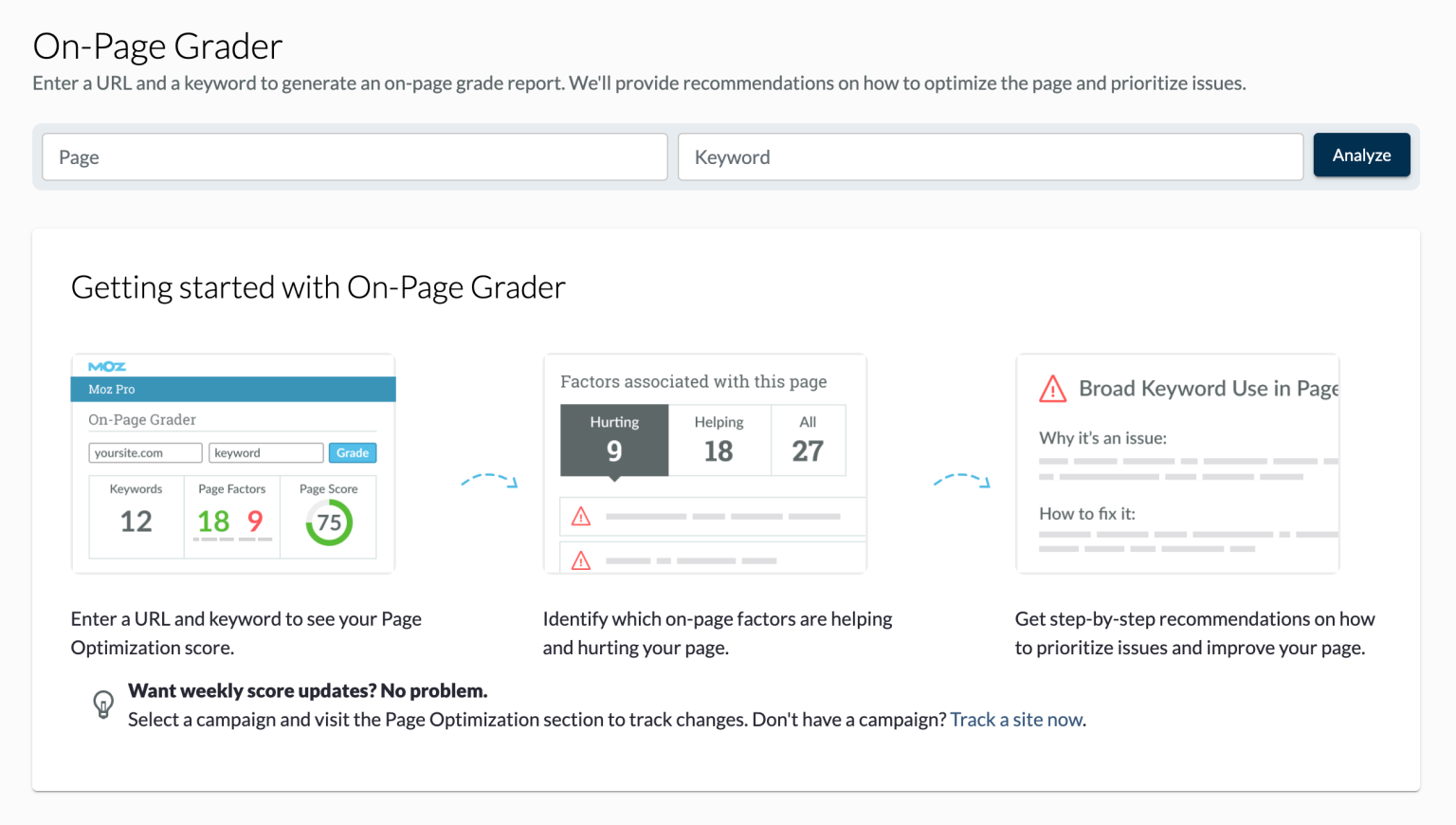
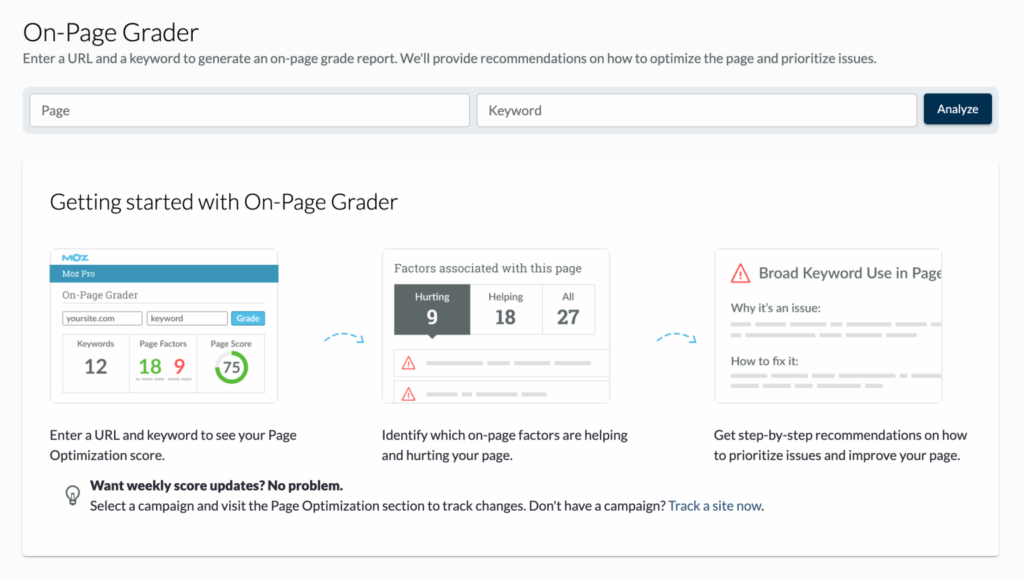
- Page Optimization Score: Moz Pro’s page optimization feature analyzes individual pages and provides recommendations to improve their SEO performance. While not solely focused on page speed, it considers factors like keyword usage, content quality, and technical SEO elements that can indirectly affect loading times.
By using these tools, you can identify areas where your website is underperforming and take steps to improve its Moz page speed.
Key Factors Affecting Moz Page Speed
Several factors contribute to a website’s page speed. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective optimization. Here are some of the most important ones:
Server Response Time
The time it takes for your server to respond to a request is a critical factor. A slow server response time can significantly impact page speed. Factors that can affect server response time include:
- Server Location: Choose a server location that is geographically close to your target audience.
- Server Resources: Ensure your server has sufficient resources (CPU, RAM) to handle traffic.
- Database Queries: Optimize database queries to reduce the time it takes to retrieve data.
- Hosting Provider: Choose a reliable hosting provider with fast servers.
Image Optimization
Large, unoptimized images can significantly slow down your website. Optimizing images involves:
- Compressing Images: Reduce the file size of images without sacrificing quality.
- Choosing the Right Format: Use appropriate image formats (JPEG for photos, PNG for graphics).
- Using Lazy Loading: Load images only when they are visible in the viewport.
- Resizing Images: Ensure images are appropriately sized for their intended display.
Code Optimization
Clean, efficient code is essential for fast page speed. Code optimization involves:
- Minifying CSS and JavaScript: Remove unnecessary characters from code to reduce file size.
- Combining CSS and JavaScript Files: Reduce the number of HTTP requests by combining files.
- Removing Unused Code: Eliminate any unused CSS or JavaScript code.
- Optimizing HTML: Ensure your HTML code is clean and well-structured.
Caching
Caching involves storing static versions of your website’s content to reduce server load and improve page speed. Types of caching include:
- Browser Caching: Allows browsers to store static assets locally.
- Server-Side Caching: Stores cached versions of pages on the server.
- CDN (Content Delivery Network): Distributes your website’s content across multiple servers to improve loading times for users in different locations.
Render-Blocking Resources
Render-blocking resources are CSS and JavaScript files that prevent the browser from rendering the page until they are downloaded and processed. To improve page speed, you should:
- Defer JavaScript: Load JavaScript files after the main content has loaded.
- Inline Critical CSS: Include the CSS necessary for rendering the above-the-fold content directly in the HTML.
- Remove Unnecessary CSS: Eliminate any CSS that is not essential for the initial rendering of the page.
How to Improve Your Moz Page Speed: Practical Strategies
Now that you understand the key factors affecting Moz page speed, let’s explore some practical strategies for improvement:
Optimize Images
Use tools like TinyPNG, ImageOptim (for Mac), or ShortPixel to compress images without losing quality. Ensure images are properly sized and use appropriate formats. Implement lazy loading to defer the loading of offscreen images.
Leverage Browser Caching
Configure your server to leverage browser caching. This allows browsers to store static assets locally, reducing the need to download them on subsequent visits. You can configure browser caching using .htaccess files (for Apache servers) or through your server’s control panel.
Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML
Use tools like UglifyJS (for JavaScript), CSSNano (for CSS), and HTMLMinifier (for HTML) to minify your code. These tools remove unnecessary characters, comments, and whitespace, reducing file sizes and improving page speed. Many content management systems (CMS) like WordPress offer plugins that automate this process.
Reduce HTTP Requests
Minimize the number of HTTP requests by combining CSS and JavaScript files, using CSS sprites (combining multiple images into a single image), and reducing the number of external resources. Each HTTP request adds overhead and can slow down your website.
Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A CDN distributes your website’s content across multiple servers located in different geographical regions. This ensures that users can access your content from a server that is close to them, reducing latency and improving page speed. Popular CDN providers include Cloudflare, Akamai, and Amazon CloudFront.
Optimize Your Database
A poorly optimized database can slow down your website. Regularly clean up your database by removing unnecessary data, optimizing tables, and caching frequently accessed data. If you’re using a CMS like WordPress, there are plugins available to help you optimize your database.
Choose a Fast Hosting Provider
Your hosting provider plays a crucial role in your website’s page speed. Choose a hosting provider that offers fast servers, sufficient resources, and reliable uptime. Consider using a dedicated server or a virtual private server (VPS) for better performance.
Implement AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages)
AMP is a Google project designed to create faster, more streamlined mobile web pages. Implementing AMP can significantly improve your website’s page speed on mobile devices. However, AMP requires you to create separate AMP versions of your pages, which can be time-consuming.
Monitor Your Website’s Performance
Regularly monitor your website’s page speed using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, and WebPageTest. These tools provide detailed insights into your website’s performance and identify areas for improvement. Use this data to continuously optimize your website for speed.
The Future of Moz Page Speed and Website Optimization
As technology evolves, the importance of page speed will only continue to grow. With the increasing adoption of mobile devices and the rise of mobile-first indexing, websites must be optimized for speed to remain competitive. Emerging technologies like HTTP/3 and QUIC promise to further improve page speed by reducing latency and improving connection efficiency.
Furthermore, the development of AI-powered optimization tools will likely automate many of the tasks involved in optimizing Moz page speed. These tools will be able to analyze website performance in real-time and automatically adjust settings to improve loading times.
In conclusion, understanding and optimizing your Moz page speed is essential for creating a successful online presence. By following the strategies outlined in this guide, you can improve your website’s performance, enhance user experience, and boost your search engine rankings. Remember to continuously monitor your website’s performance and adapt your optimization strategies to stay ahead of the curve. [See also: Website Speed Optimization Techniques] [See also: Mobile SEO Best Practices]